top of page


Nicole M, Maddie B, Jordan, Shelly, Maddie G, Emma, Nora
Interval and Radius of Convergence
Example #1
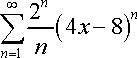
Similar to the Ratio Test, plug in the sigma notation into the Ratio Test General Formula.
Expand.
Cancel out the repetitive parts.
Factor out the parentheses in the numerator. Take the limit.
Using 'Principle of Dominance', the limit of the problem is 2. Ultimately, we achieve 2|4x-8|.
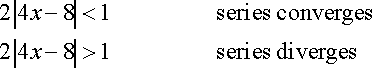
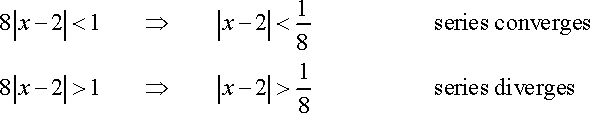
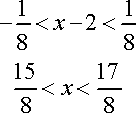
The Radius of Convergence is found by placing the answer (2|4x-8|) into an inequality constrained from (-1,1) and solving for until there is no coefficient for 'x'.
Revised Constraints
Proof of Convergence/Divergence of the Revised Constraints
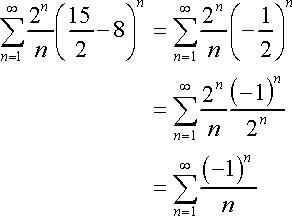
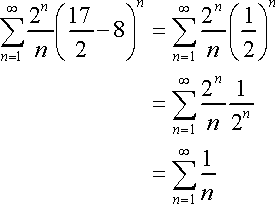
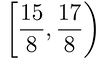
Interval of Convergence is found when the Revised Constraints are discovered. In order to determine between a bracket [ , ] or parentheses ( , ), first determine whether each value converges/diverges. If the value converges (when plugged back into the original sigma notation), use a bracket. If the value diverges (when plugged back into the original sigma notation), use parentheses.
Therefore, '15/8' converges and '17/8' diverges.
bottom of page